© 2014-2023 Aliaksandr Drozd

inventions
that have changed
the world
that have changed
the world
Huawei's policy is to bring people closer through technology. By investing in technology development, the company brings together a huge cluster of scientists and inventors from all over the world in order to make human life even more comfortable and safe. Invention and innovation have become the main vector of Huawei's development until 2025. A lot of efforts have already been made to introduce, for example, 5G data transmission technology, and this is just the beginning.
Invention as a constant engine of progress has become the main theme of the annual Huawei calendar for 2018. I selected 12 discoveries and inventions that have changed the viewpoint of mankind on this world. These inventions became a pivotal point in the development of engineering and technology, gave rise to new sciences and areas of research. These discoveries made it possible to expand the limits of human capabilities so that’s why we began to look at this world even wider.
concept
inventors
12
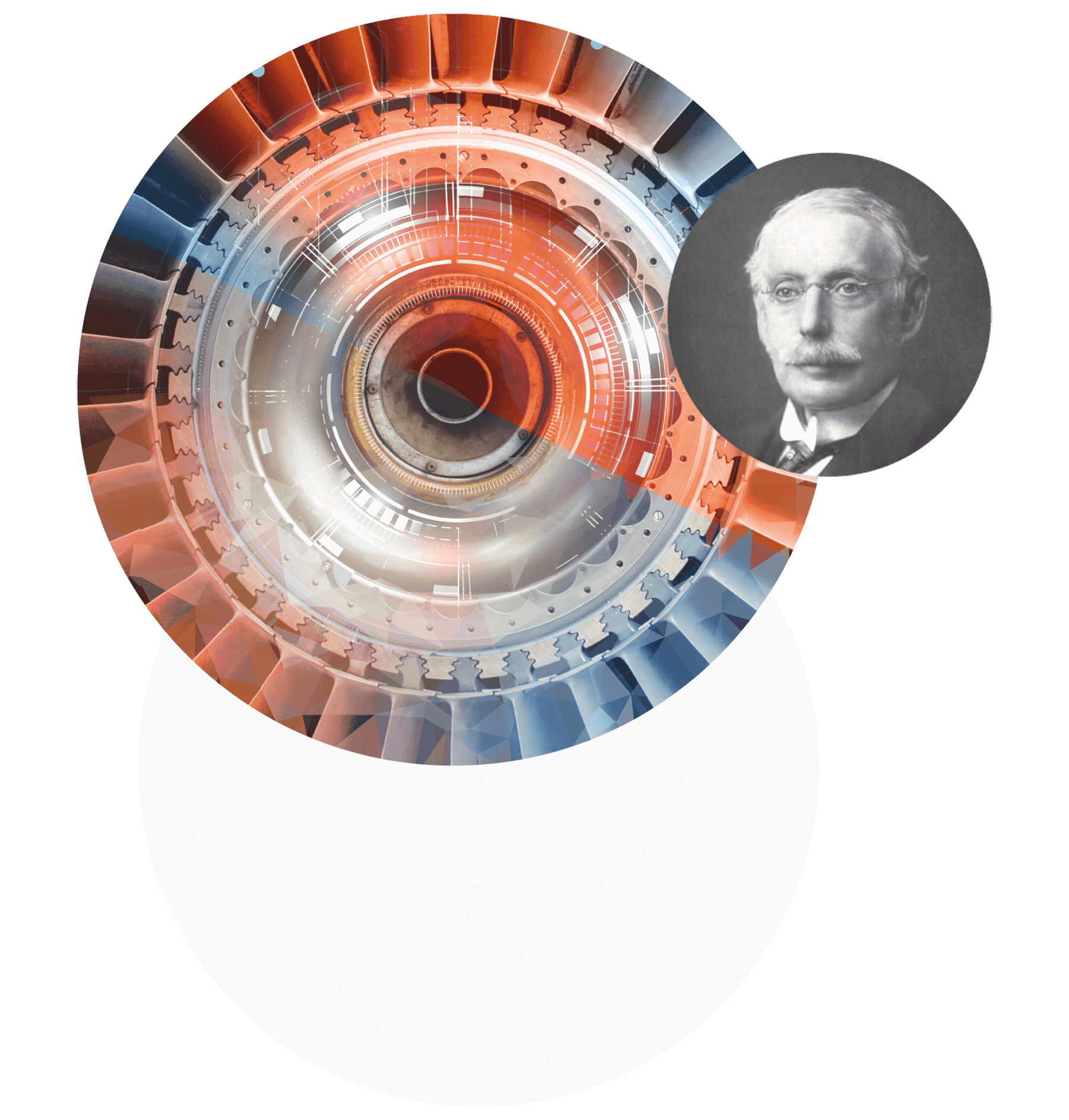
Charles Algernon Parsons
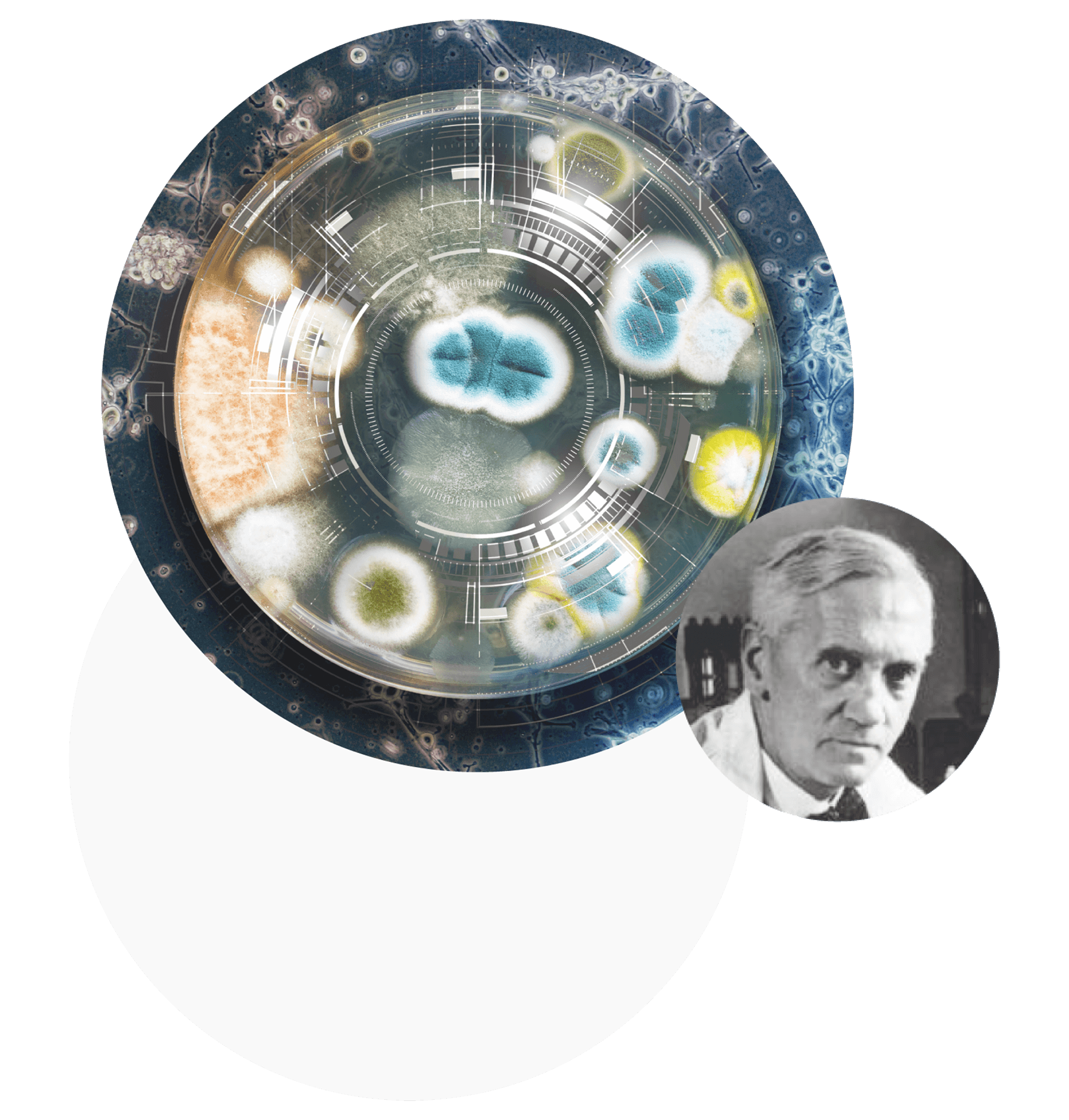
Alexander Fleming
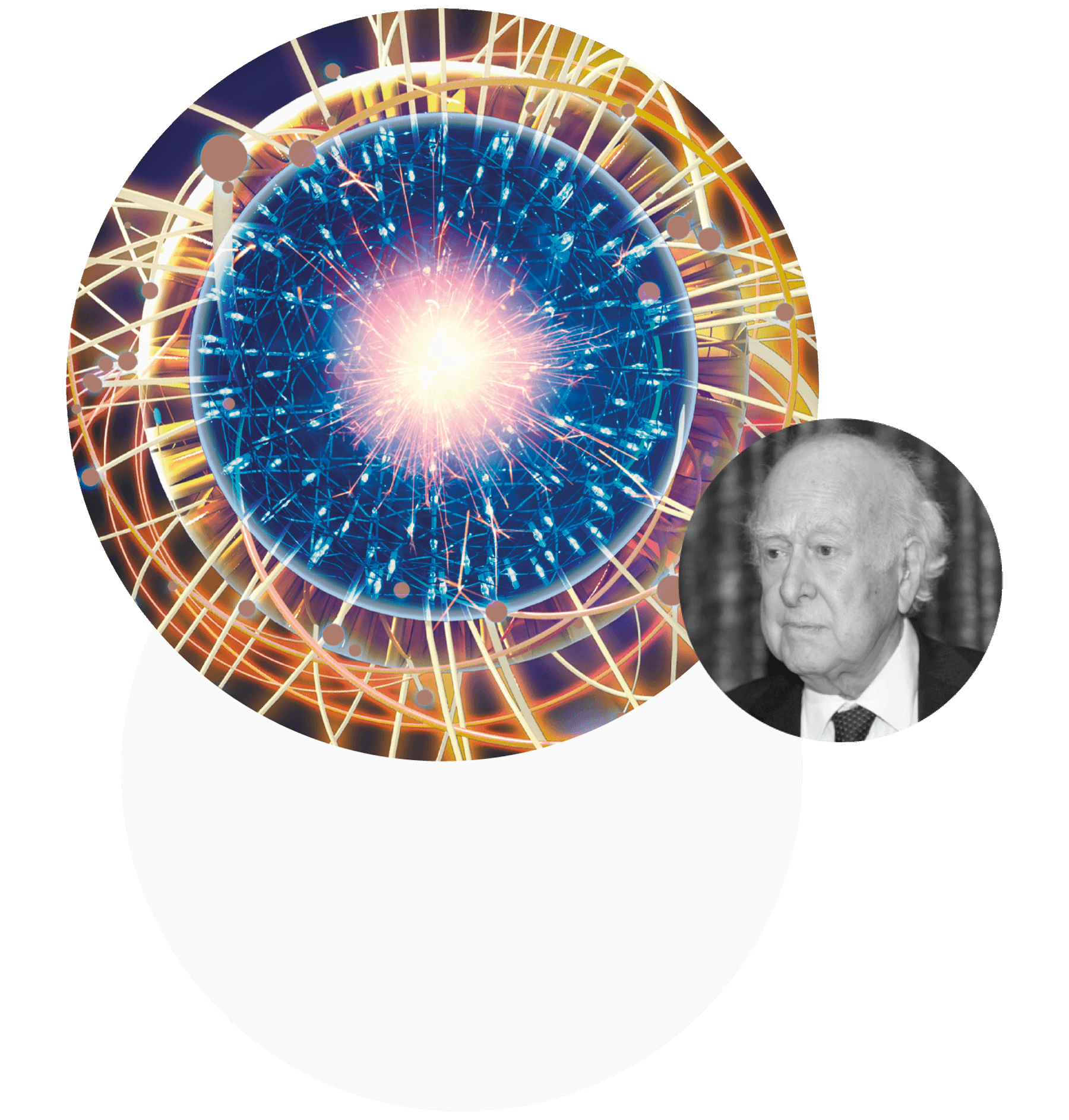
Peter Ware Higgs
Wilbur and Orville Wright
Dmitri Mendeleev
Nikola Tesla
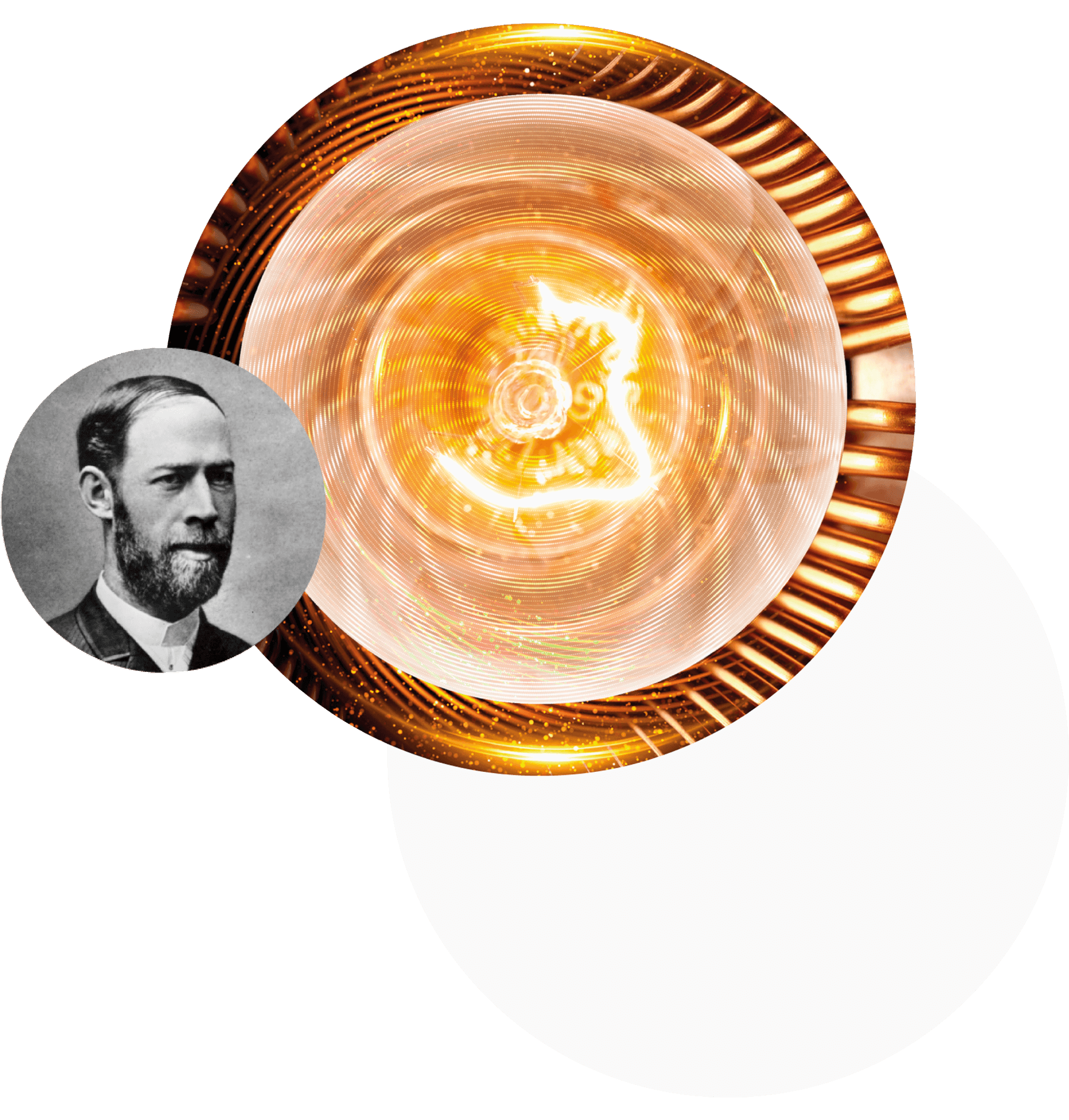
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
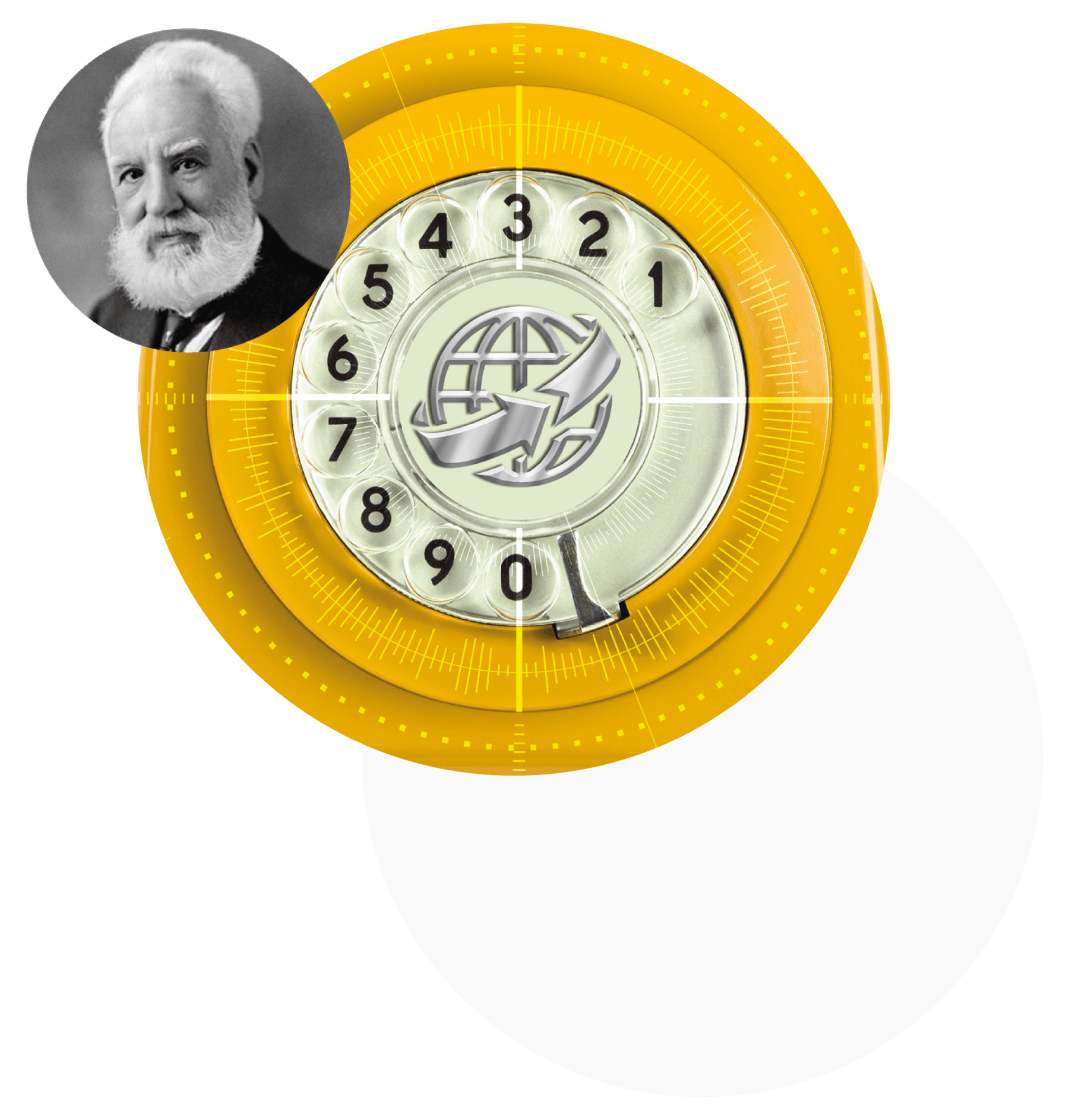
Alexander Graham Bell
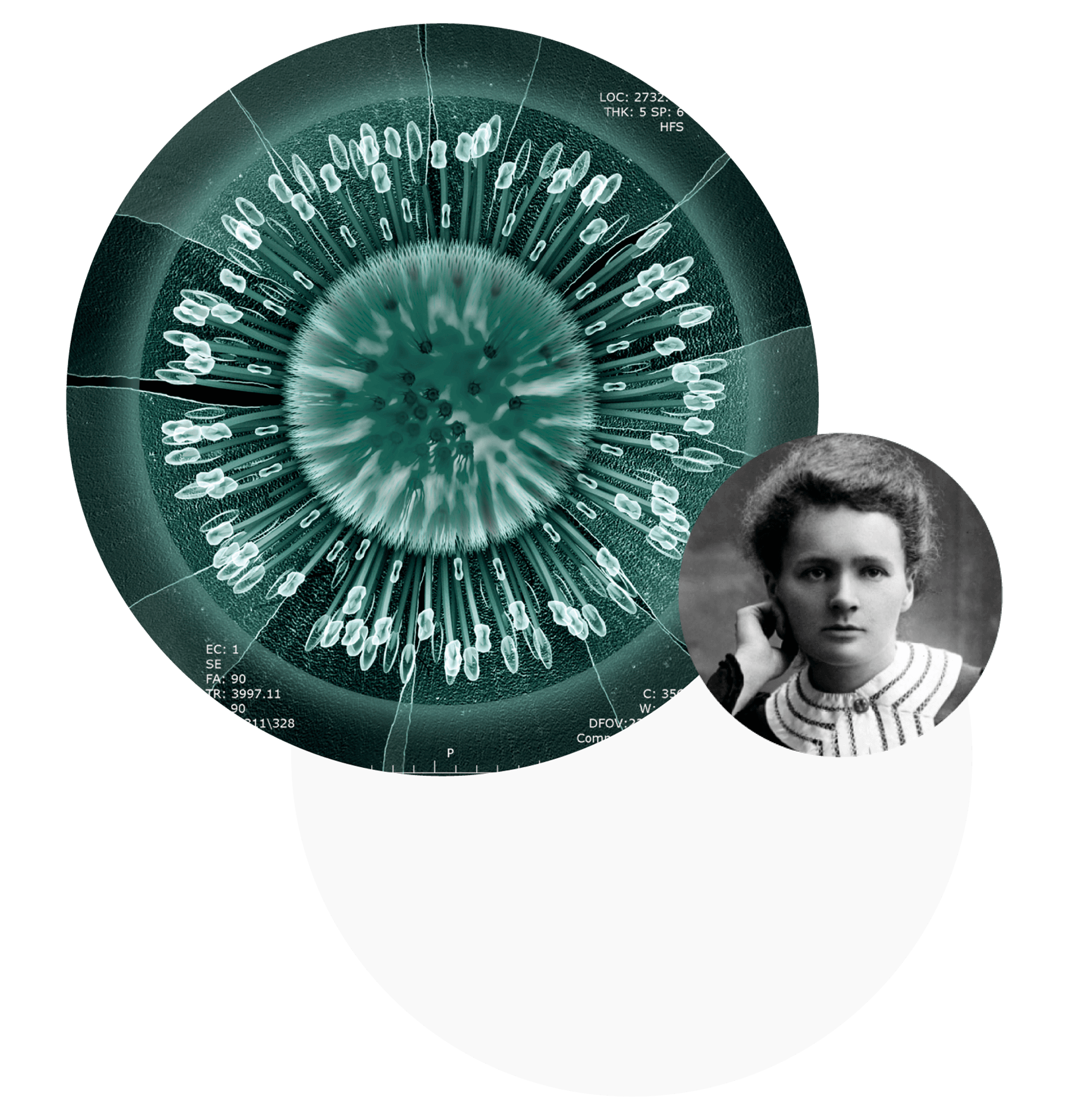
Maria Skłodowska-Curie
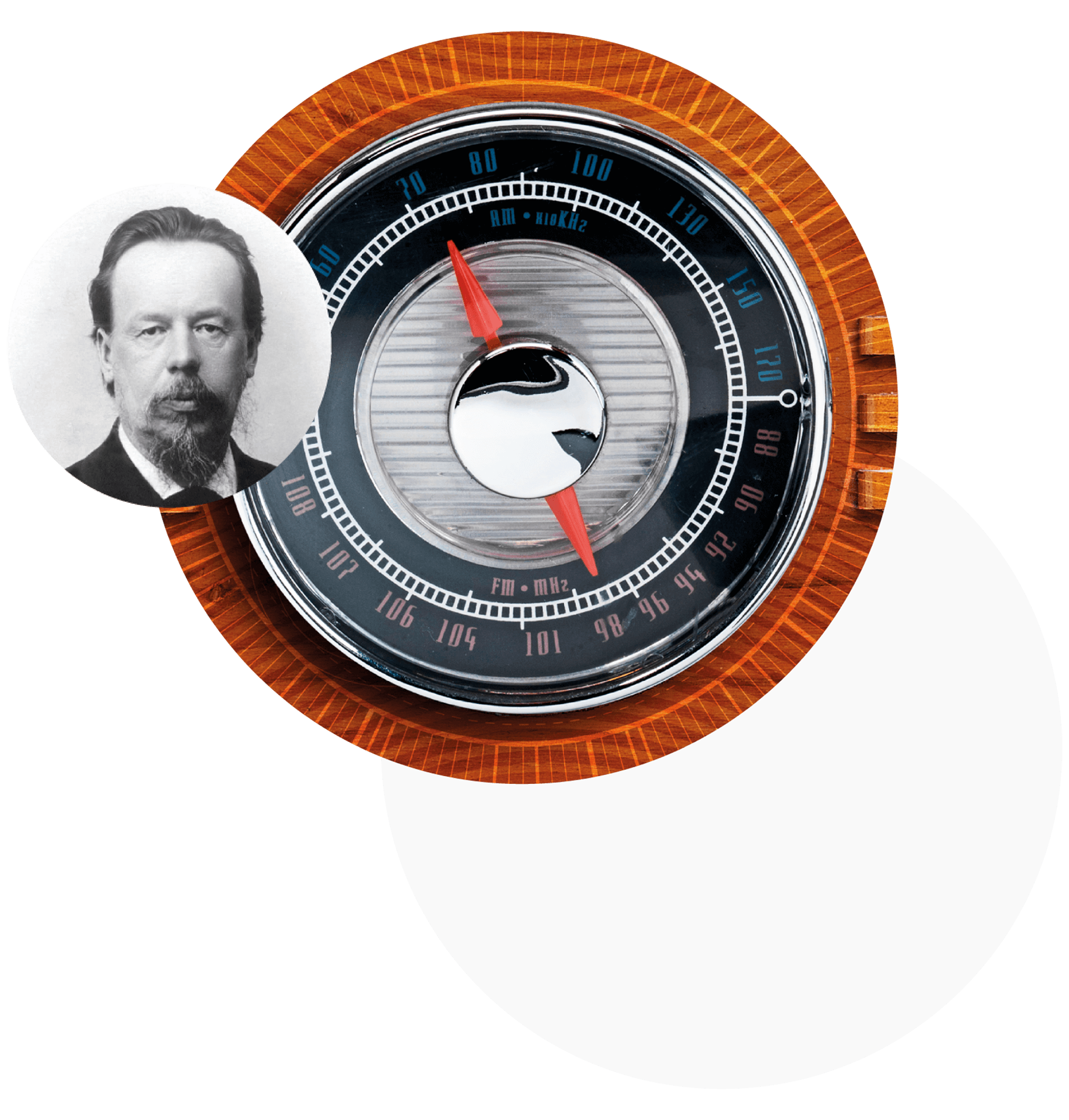
Alexander Popov
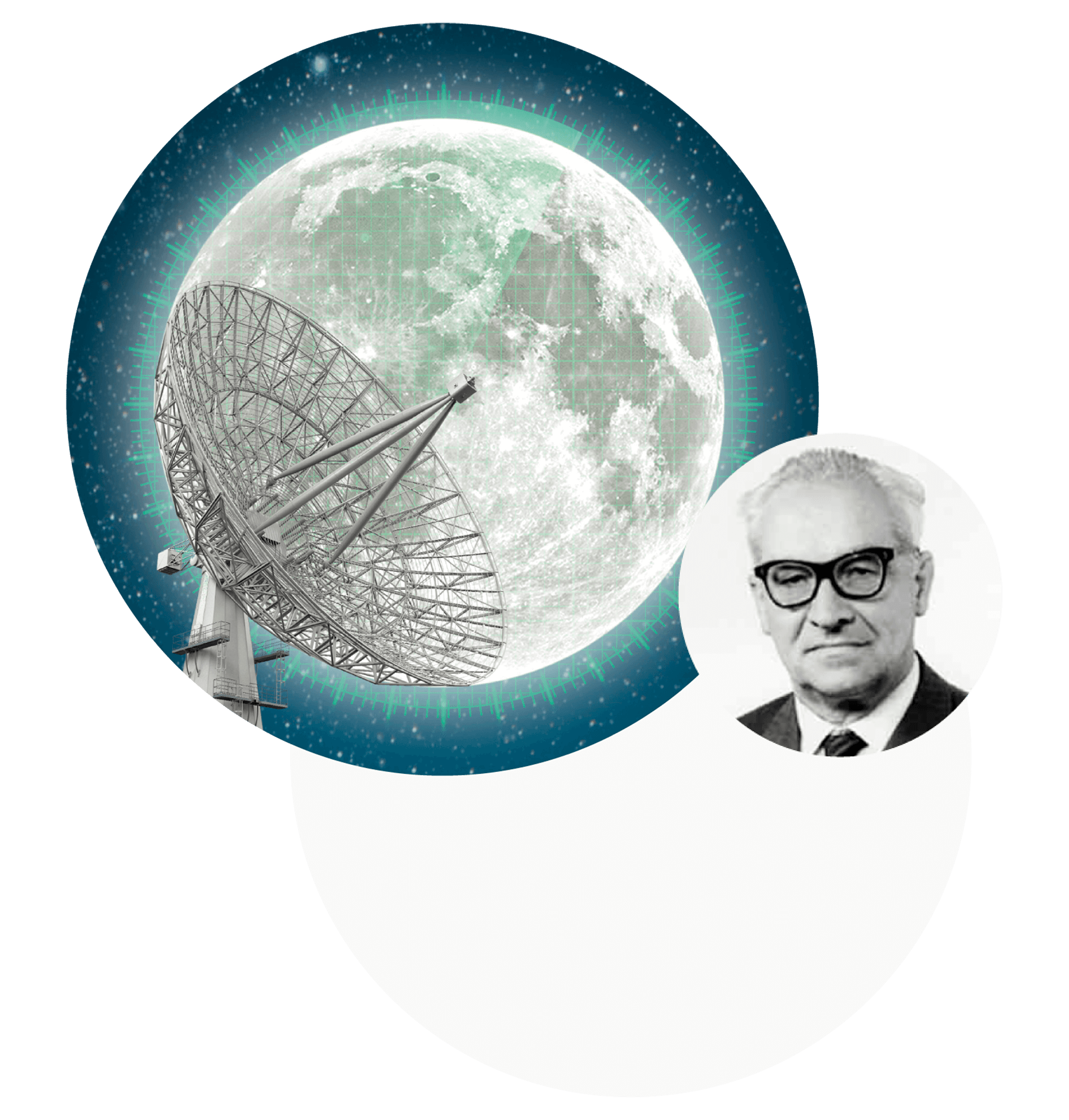
Vladimir Kotelnikov
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky

















A British structural engineer and an industrialist, he invented and patented the multi-stage jet steam turbine, known as the Parsons turbine. This turbine in a modified form is still used in modern energy. His scientific ideas also had a significant impact on the development of the aviation industry and jet engines.
A Russian physicist and an electrical engineer, a professor, an inventor, an honorary electrical engineer, in Russia, Alexander Popov is given priority in the invention of the radio: in 1895, he demonstrated the receiver he created at a meeting of the Physics Department of the Russian Physics-and-Chemistry Society. In honor of this, May 7 is celebrated annually as the Radio Day.
An inventor in the realm of electrical and radio engineering, he studied alternating electric current and devices operating on it, in many ways running ahead of his time. For example, Tesla was convinced that electricity and energy could be transferred directly, but only recently have we managed to conceive wireless chargers to prove his rightness.
A scientist, an inventor, a founder of theoretical astronautics, he created conceptual models of a liquid-propellant rocket for space flight, and "rocket trains", prototypes of multi-stage rockets. Tsiolkovsky derived a formula for calculating the amount of fuel to achieve the desired speed and set up the principles of ballistic missile design.
The world's first twice Nobel laureate, the only woman to win the Nobel Prize twice, and the first female teacher in the history of the Sorbonne. Together with her husband Pierre Curie, she discovered radium, polonium and the phenomenon of radioactivity. The couple did not receive a patent for the discovery, providing it free of charge for the benefit of mankind.
A German physicist who experimentally confirmed Maxwell's electromagnetic theory of light and proved the existence of electromagnetic waves. The obtained results formed the basis for the creation of the radio. For the first time, he observed and described the external photoelectric effect, gave the derivation of the general theorems of mechanics and its mathematical apparatus. The unit of frequency is named after Hertz.
A scientist and an inventor, he created and in 1876 patented a telephone, the handset of which served alternately for transmitting and receiving human speech. For a long time he was considered the inventor of the telephone, but in 2002 the US Congress recognized that the championship belongs to the Italian Antonio Meucci, who created a device that transmits sounds over wires.
A radio physicist, a radio engineer, a computer scientist, a radio astronomer, and a cryptographer, he developed the theory of digital signal processing, creating the sampling theorem, which in the Russian-language literature bears his name, and in the English-language literature is named after Nyquist and Shannon. Kotelnikov improved methods of radio reception and also studied radio interference and ways to solve them.
A Russian encyclopedic scientist who excelled in many scientific disciplines, but is best known for his creation of the Periodic Table of Chemical Elements. He also studied silicates, gases and solutions, wrote the first Russian textbook on organic chemistry and was at the origins of Russian meteorology.
A British theoretical physicist, a Nobel laureate, who is best known for the mechanism he proposed for explaining the origin of the mass of elementary particles (including the Higgs boson), which is considered one of the main components of the Standard Model. It describes electromagnetic, weak and strong interaction of all elementary particles.
The Wright brothers became the world's first designers and builders of an aircraft on which they made a controlled experimental flight. By discovering the three-axis rotation method, they were able to steer the aircraft and effectively control its balance and maneuverability. Aircraft control is based on this scheme even to this day.
A British bacteriologist. He discovered lysozyme, a natural antibacterial enzyme for humans, and isolated penicillin from the fungi Penicillium notatum, which became the world's first antibiotic. Receiving the Nobel Prize, Fleming modestly noted that he "did not invent penicillin, but only drew people's attention to it and gave it a name."
inventors
12
Charles Algernon Parsons

Alexander Fleming
Peter Ware Higgs
Wilbur and Orville Wright
Dmitri Mendeleev
Nikola Tesla
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz
Alexander Graham Bell
Maria Skłodowska-Curie
Alexander Popov
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky












Vladimir Kotelnikov

kv

calendar

set









turbine
penicillin
Higgs boson
airplane
astronautics theory
radio transmission
tesla coil
periodic table
radio
radioactivity
telephone
electromagnetic waves


Huawei traditionally pays huge attention to research and development. The company annually invests more than 10% of its sales revenue in science and technology. In 2016 alone, Huawei allocated $11 billion for this purpose. The representative office of the company in the Eurasian market asked to create a calendar, which is traditionally given to the company's employees and partners. To emphasize the innovative focus and scientific approach of the company, I chose the most significant inventions in the history of mankind. The client was amazed at how originally and inventively the composition of each page of the calendar was created.
Concept
Print
Copywriting
Visualization
Packaging
Prepress
Copywriting
Visualization
Packaging
Prepress